What are Fat Digestion Disorders?
Individuals with fat digestion and absorption disorders often need to restrict the consumption of conventional fats in their diet because their bodies cannot utilize them adequately. To compensate for this energy deficiency, MCT fats are often recommended as they can be digested more rapidly and efficiently than conventional fats. MCT fats pass directly through the intestinal mucosa into the blood and then to the liver, where they are preferentially metabolized compared to conventional fats. (1).
But what are MCT fats and what are their benefits?
Fat-reduced diets:
Highly fat-reduced diets can lead easily to a lack of energy and consequently to weight loss.
MCT fats:
MCT fats are easier to digest than conventional fats because they passively diffuse from the GI tract without the need for digestive enzymes. They can therefore be used as alternative energy sources.
Kanso products:
Kanso MCT oils and MCT products can be easily integrated into the diet. They also help to transport fat-soluble vitamins.
Learn more...
Indications for MCT fats
Diesases of the pancreas

Enzymes produced in the pancreas play an important role in fat digestion. If the pancreas is impaired, this can lead to an enzyme deficiency. Fat digestion is therefore impaired. Since MCT fats can be directly absorbed independent of these enzymes, they play an important role in the diet of pancreatic disorders (1).
Diseases: Acute pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
Diseases of the stomach

After a (partial) removal of the stomach, food may enter the small intestine too quickly and in too large quantities, causing stomach pain, nausea and diarrhea (also called dumping syndrome). In addition to eating smaller, more frequent meals, it is often recommended to avoid high-fat and high-sugar foods. MCT fats are more easily absorbed and can help stabilize blood sugar. Therefore, they can play an important role in the diet of dumping syndrome (2).
Disease: Dumping syndrome
Diseases of the intestine

MCT fats are absorbed faster and easier because they require fewer enzymes to process. This helps reduce digestive discomfort and improve nutrient absorption. As a gentle source of fat, they can also help prevent malnutrition and optimize nutritional therapy for intestinal disorders (1). Please consult your physician or nutritional therapist for best results.
Diseases: Chronic intestinal failure, short bowel syndrome
Diseases of the liver and bile ducts

MCT fats can be used as an alternative source of fat energy for liver and bile duct disorders. They are easily digestible and do not require bile acids. This promotes nutrient absorption, increases energy intake and thus can prevent weight loss (3). Please consult your physician or nutritional therapist for best results.
Diseases: Alagille syndrome, chronic liver disease, cirrhosis of the liver
Diseases of the lymphatic vessels

In diseases of the lymphatic vessels, lymphatic pressure is increased. Replacing long-chain triglycerides (LCT) with MCT fats, whose transport does not involve the lymphatic system, provides a reduction in lymphatic pressure (1).
Diseases: Chylothorax, chylaskos, enteral protein loss syndrome
How are Fat Utilization Disorders treated?
Low fat diet

Dietary therapy for fat utilization disorders aims to reduce daily consumption of conventional fats, with tolerated fat levels varying according to underlying disease and individual factors.
Supplementation of MCT fats

Due to the restriction in the intake of LCT fats, the body requires other sources of energy. Therefore, the supplementation of MCT fats is recommended. These provide an alternative energy source and support the transport of fat-soluble vitamins (6).
Fat digestion
Digestion and metabolism of fats

The digestion of fats already begins in the mouth but primarily takes place in the duodenum (small intestine), where special enzymes (known as lipases) further break down the fats into fatty acids and glycerol ready for absorption (4).
Benefits of MCT fats in digestion and metabolism
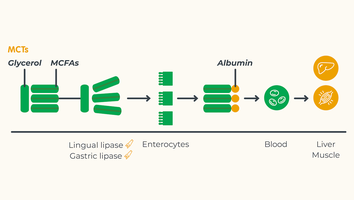
Medium-chain fatty acids (MCTs) have a shorter chain length, which gives them higher water solubility compared to conventional dietary fats (LCT fats). In the intestine, MCT fats passively diffuse into the portal system, even in the absence of digestive enzymes or reduced bile acid production. MCT fats pass from the portal system to the liver, and unlike conventional fats do not require additional transporters making them easier to metabolize (5).









